Pakeloservices
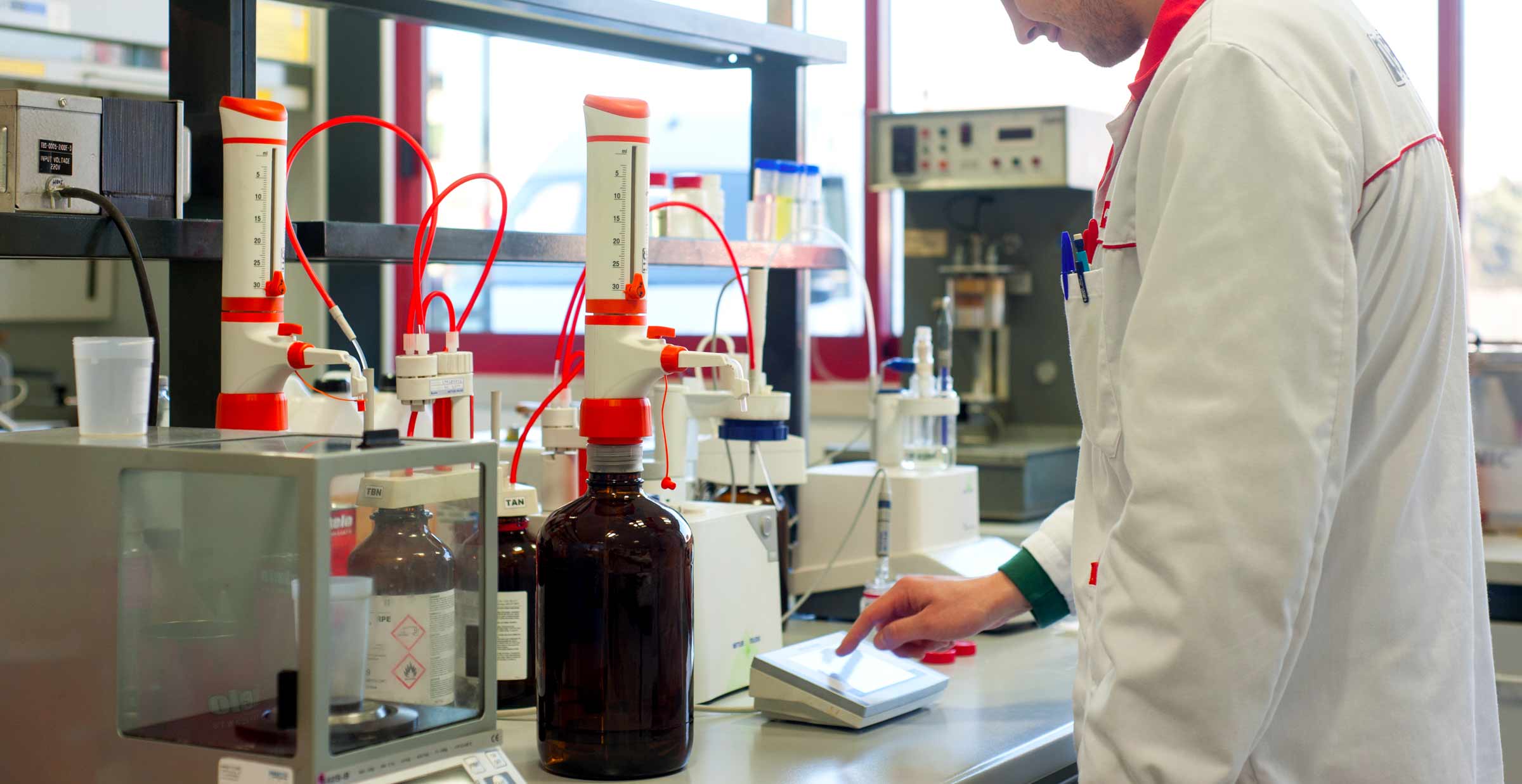
Pakelo oil analysis laboratory

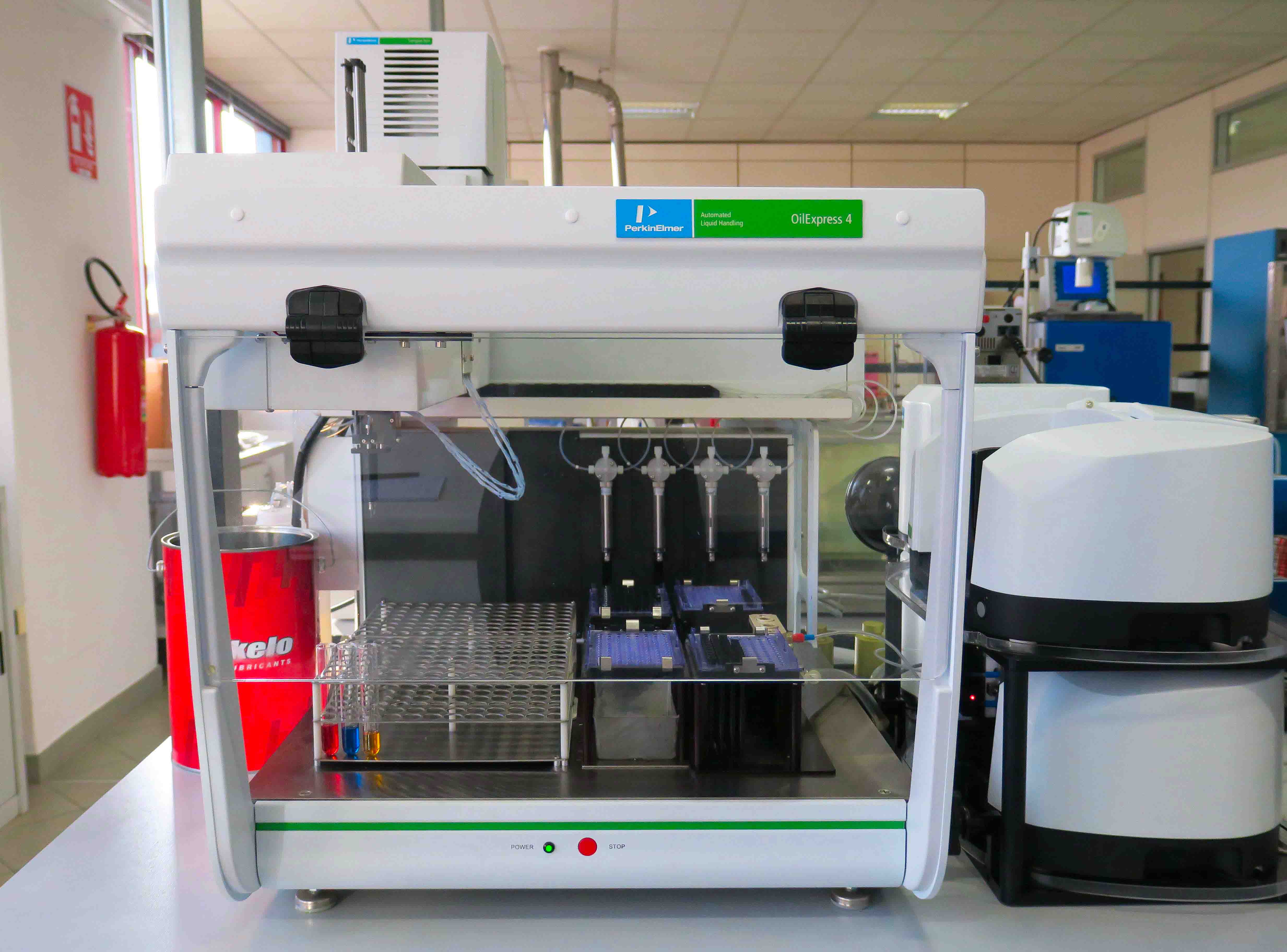
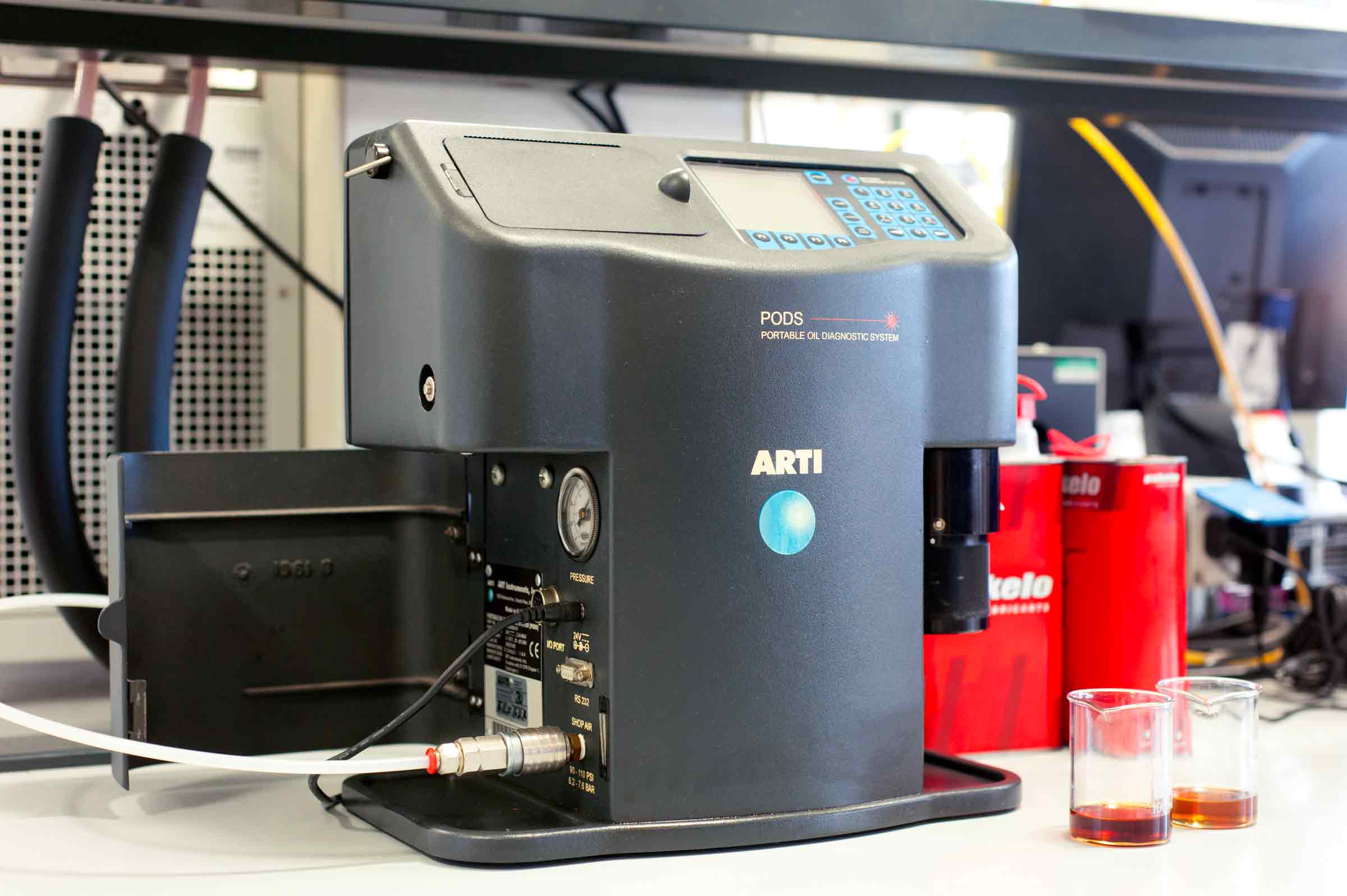
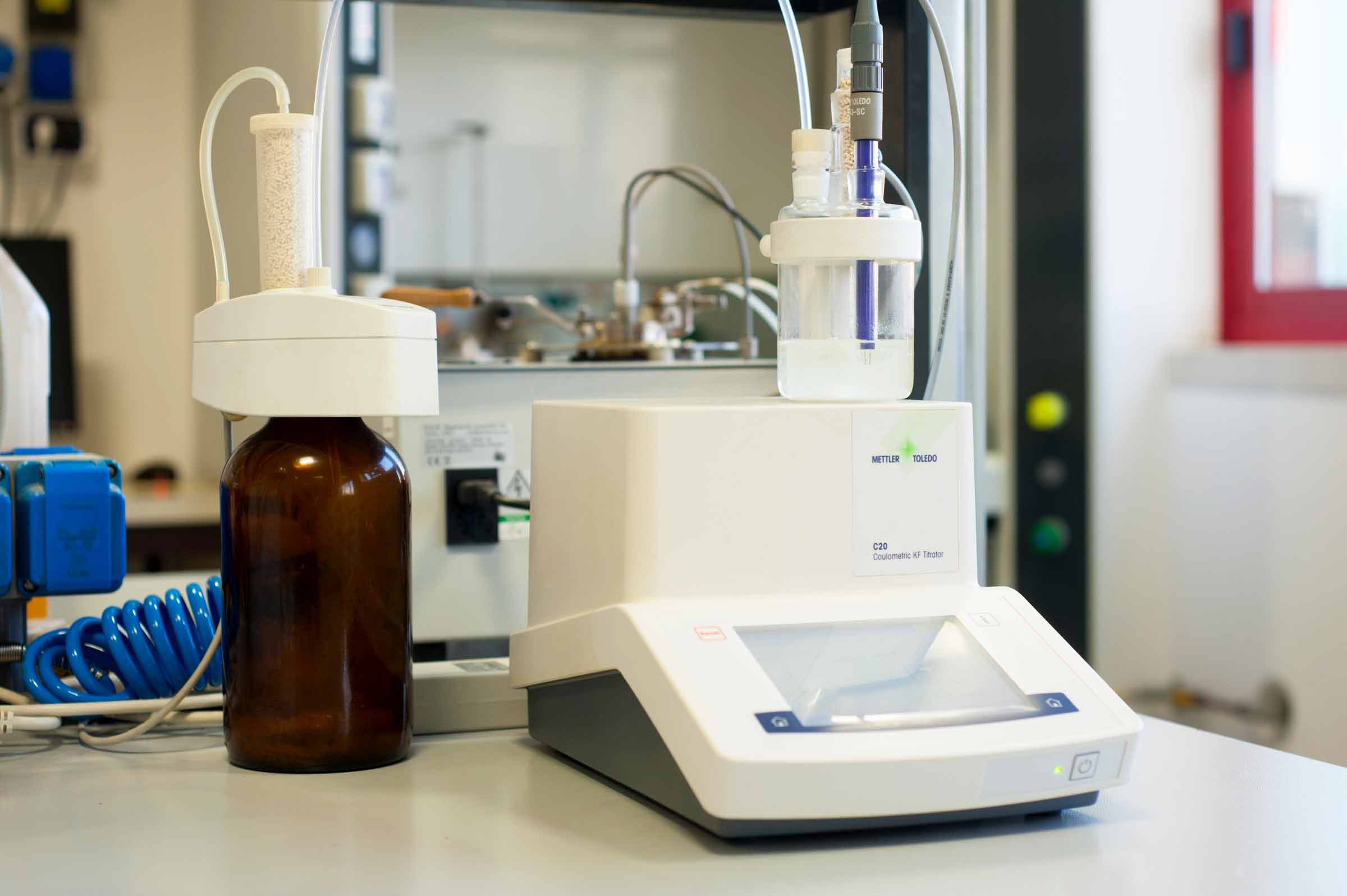
PakeloLab Equipments

R&D Equipments

Last 5 years preventive analysis trend
Tools
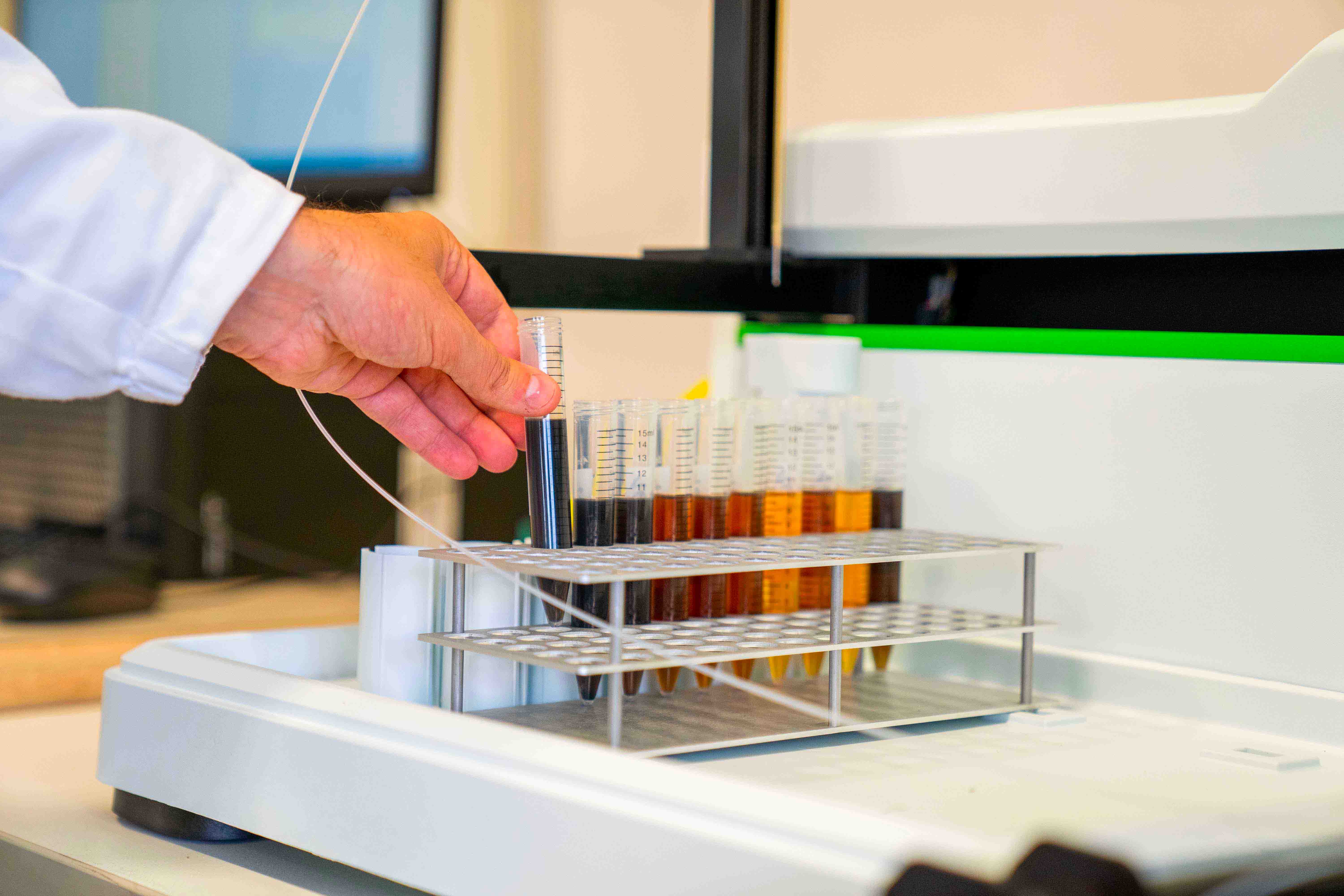
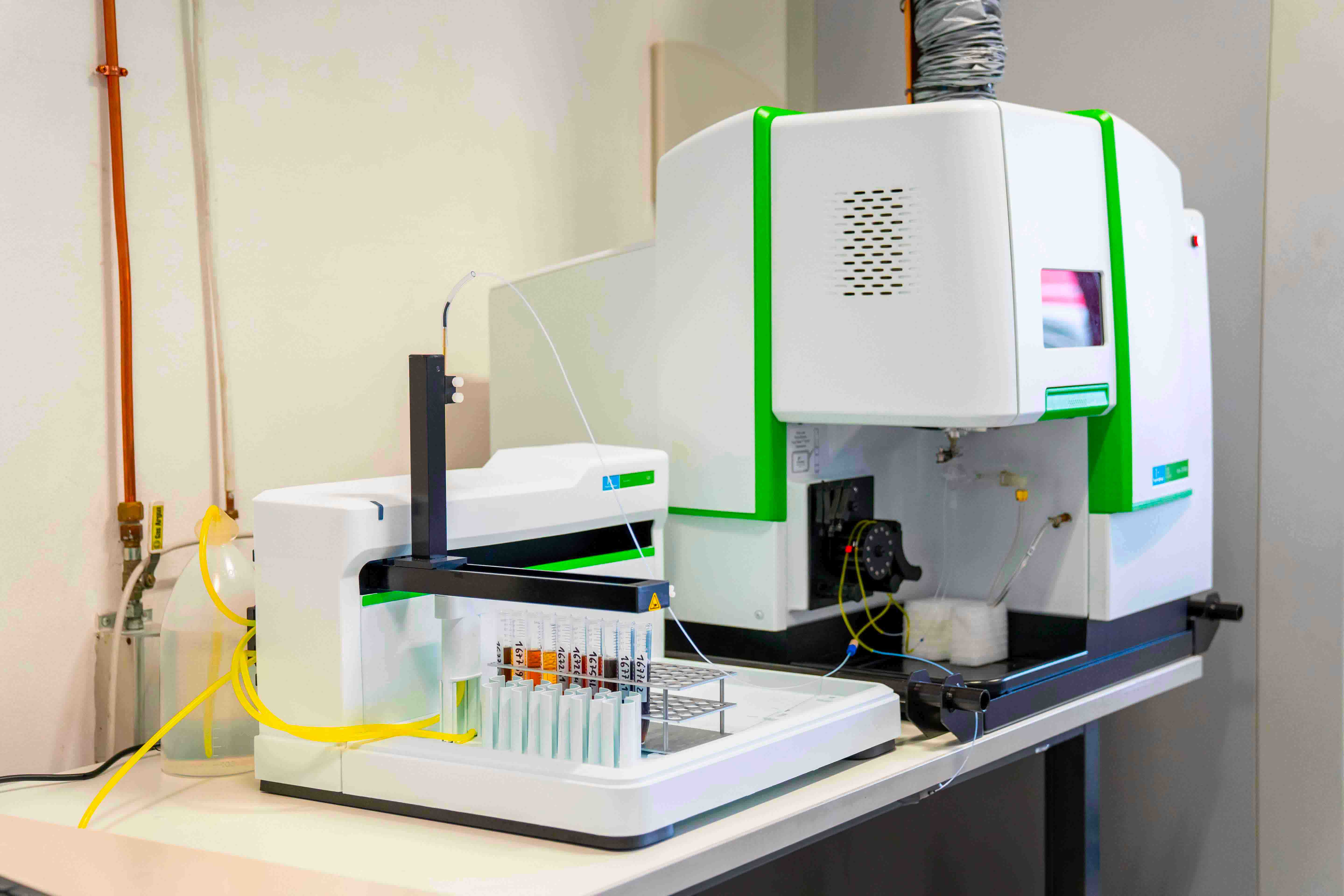
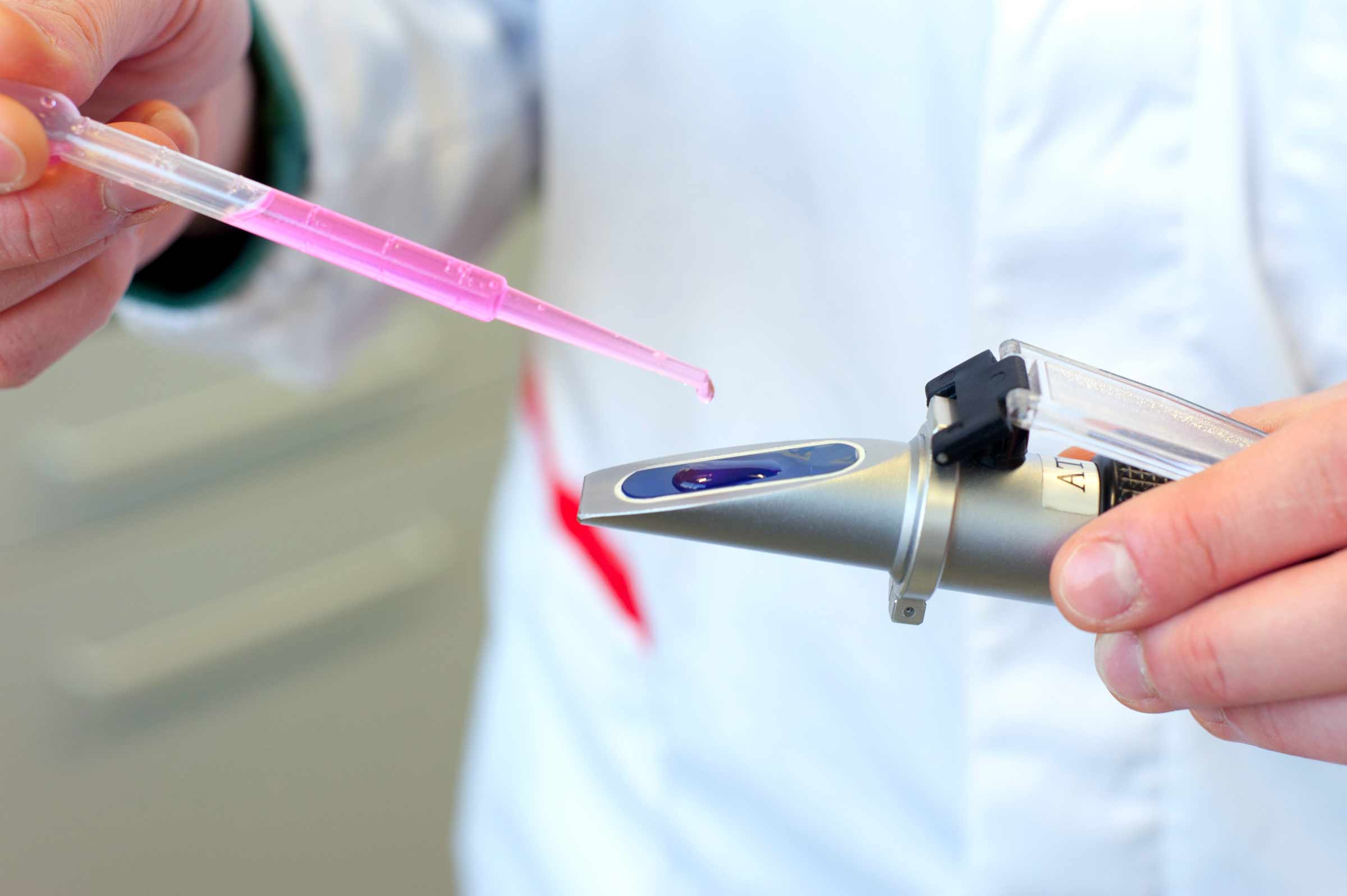
Lubricants work deeply in contact with metal surfaces of mechanical components thus they incorporate all the released wear elements. The inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry measures this content in ppm (parts per million). Resulting values estimate lubrication and mechanical parts’ conditions. This determination also helps to understand the additives depletion.
Wear Elements
Iron – Boron – Copper – Barium – Chromium – Calcium – Aluminium – Magnesium – Lead – Sodium – Silicon – Phosphorus – Zinc
Other metals
Manganese – Molybdenum – Nickel – Tin - Titanium
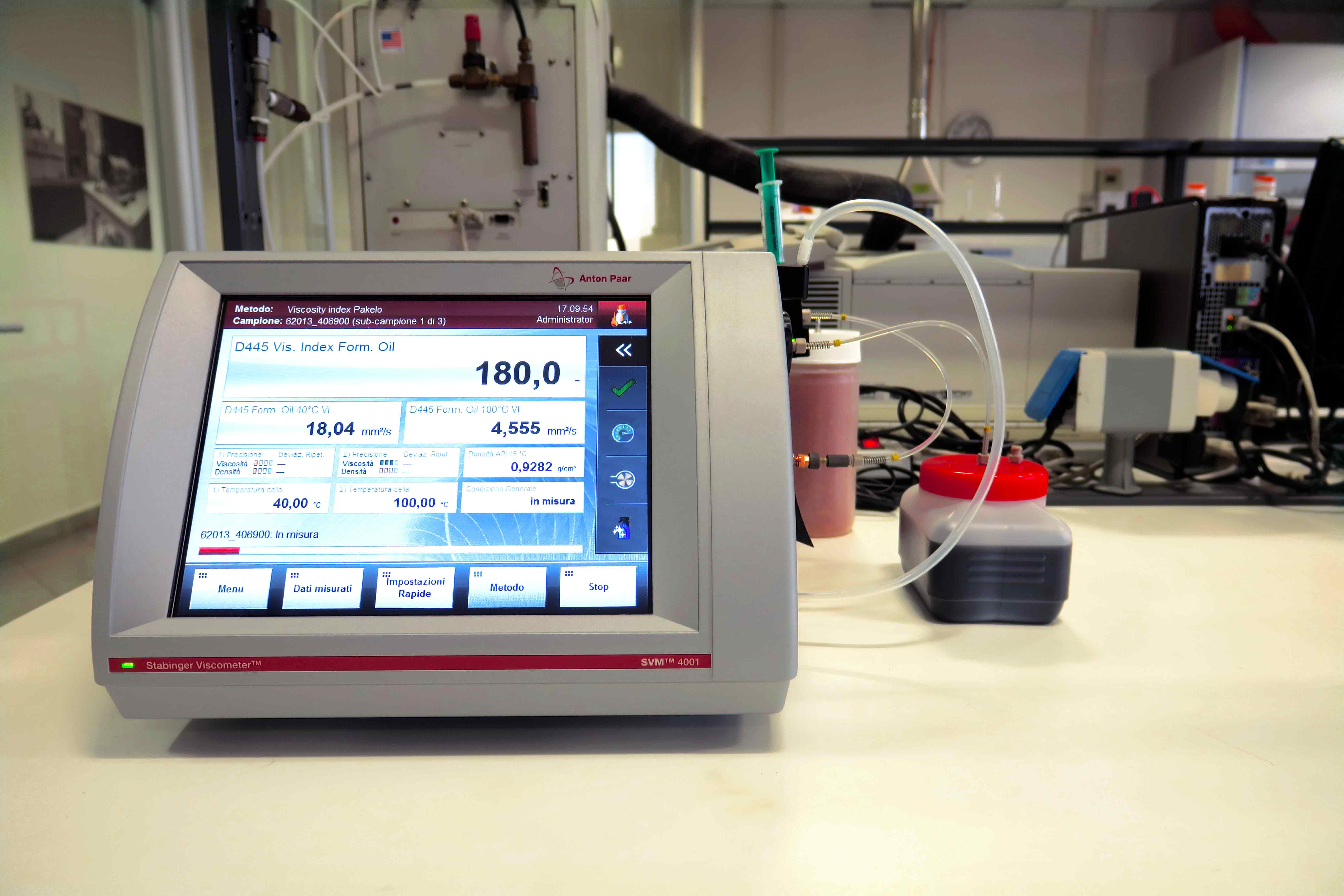
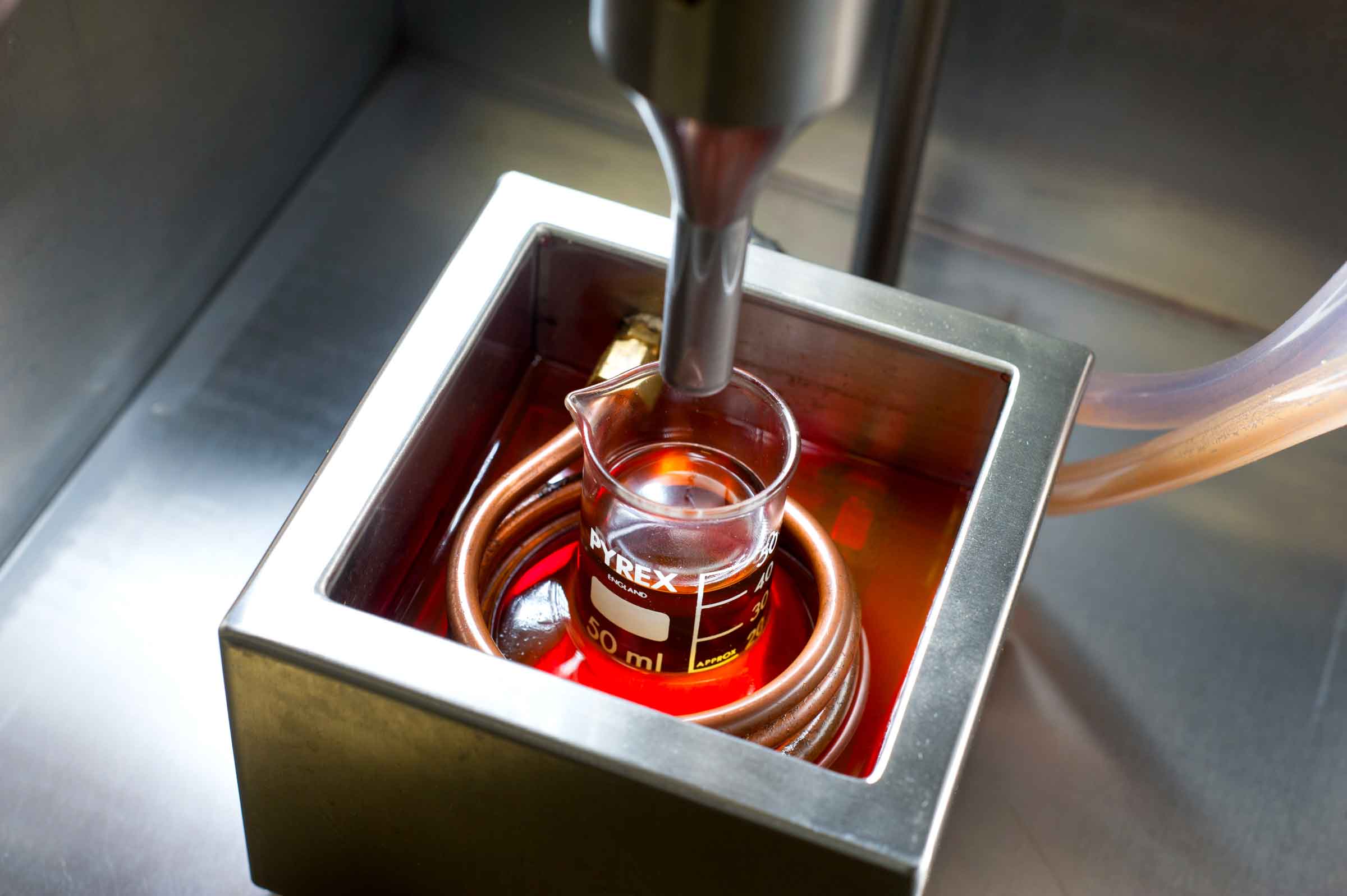
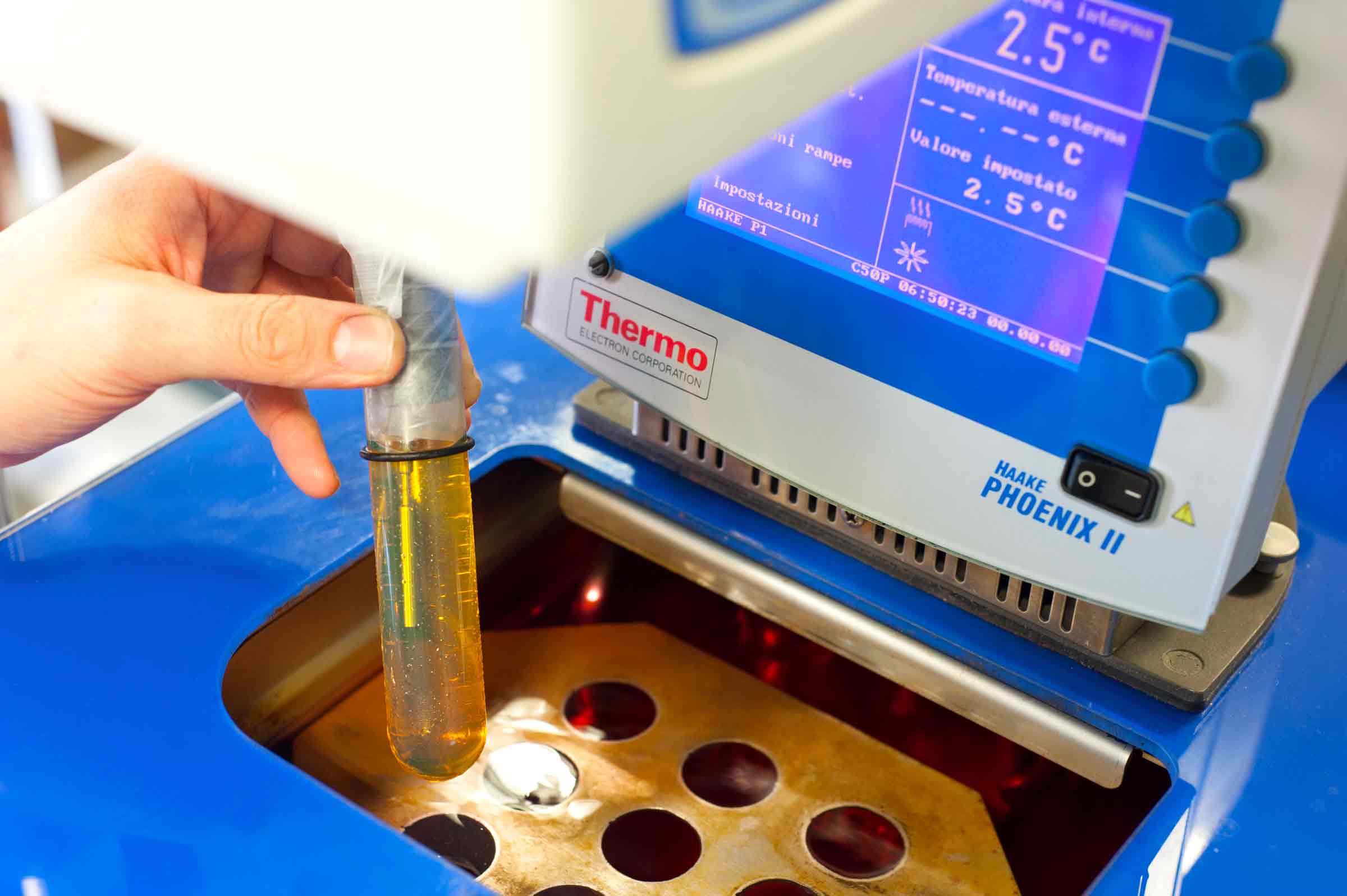
Viscosity defines oil inner friction and it indicates the Hydrodynamic Floating Capacity. The parameter is obtained by measuring the time it takes to the lubricant to flow through a calibrated capillary.
The measure is made in a thermostatic bath at the temperature of: 40°C / 104°F - ISO 3448 Class (for hydraulic and reduction units’ oils) 100°C / 212°F - SAE J300 / J306 classifications (for engine and transmission oils)
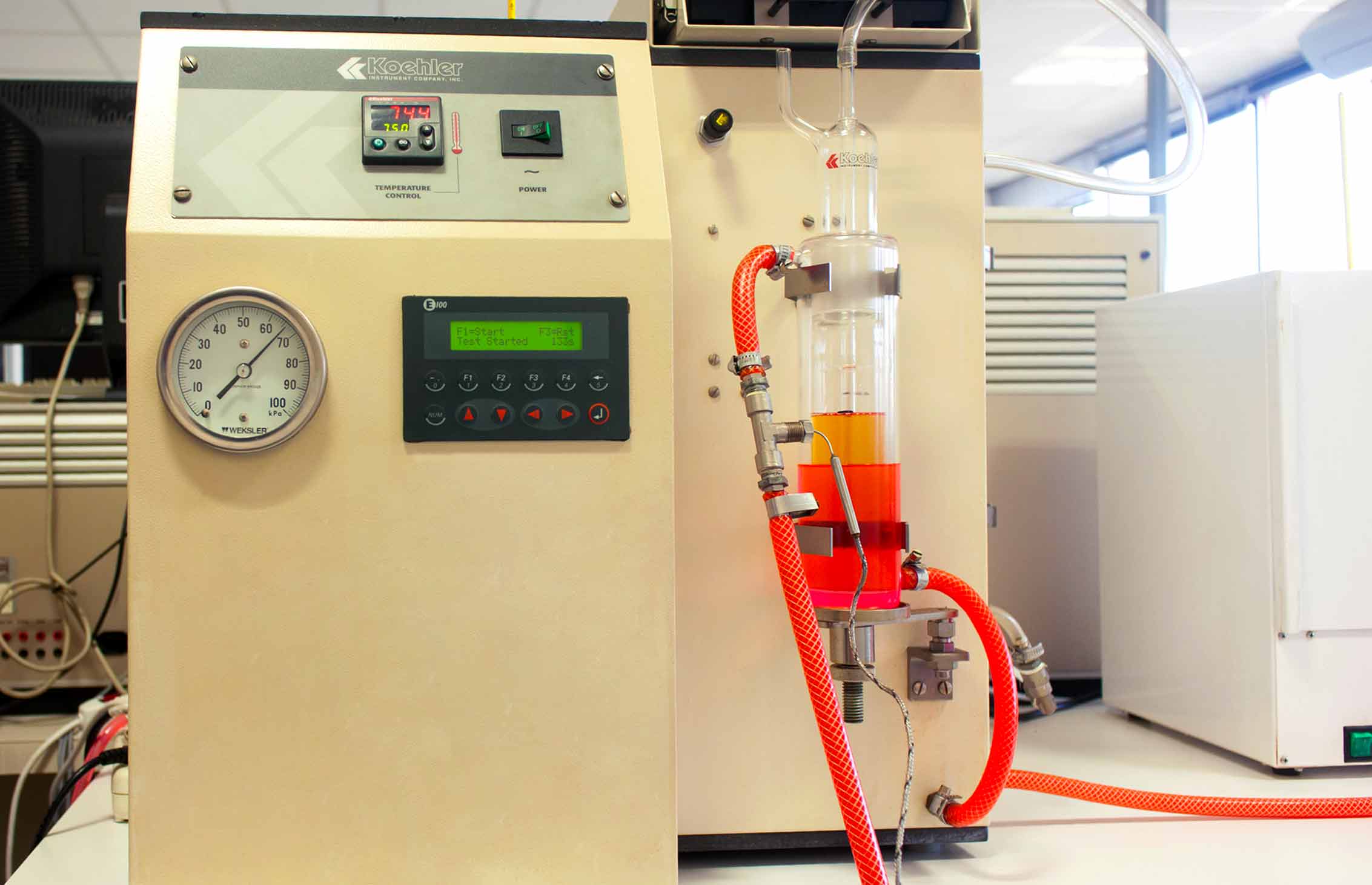
This sophisticated tool determines the organic composition by a Infra-Red spectroscopic analysis (Fourier Transform Infrared Spectroscopy). The instrument is equipped with a specific software for used oils analysis which applies the J.O.A.P. Method (Joint Oil Analysis Program).
A single IR measurement will provide information about the level of the following parameters in the oil:
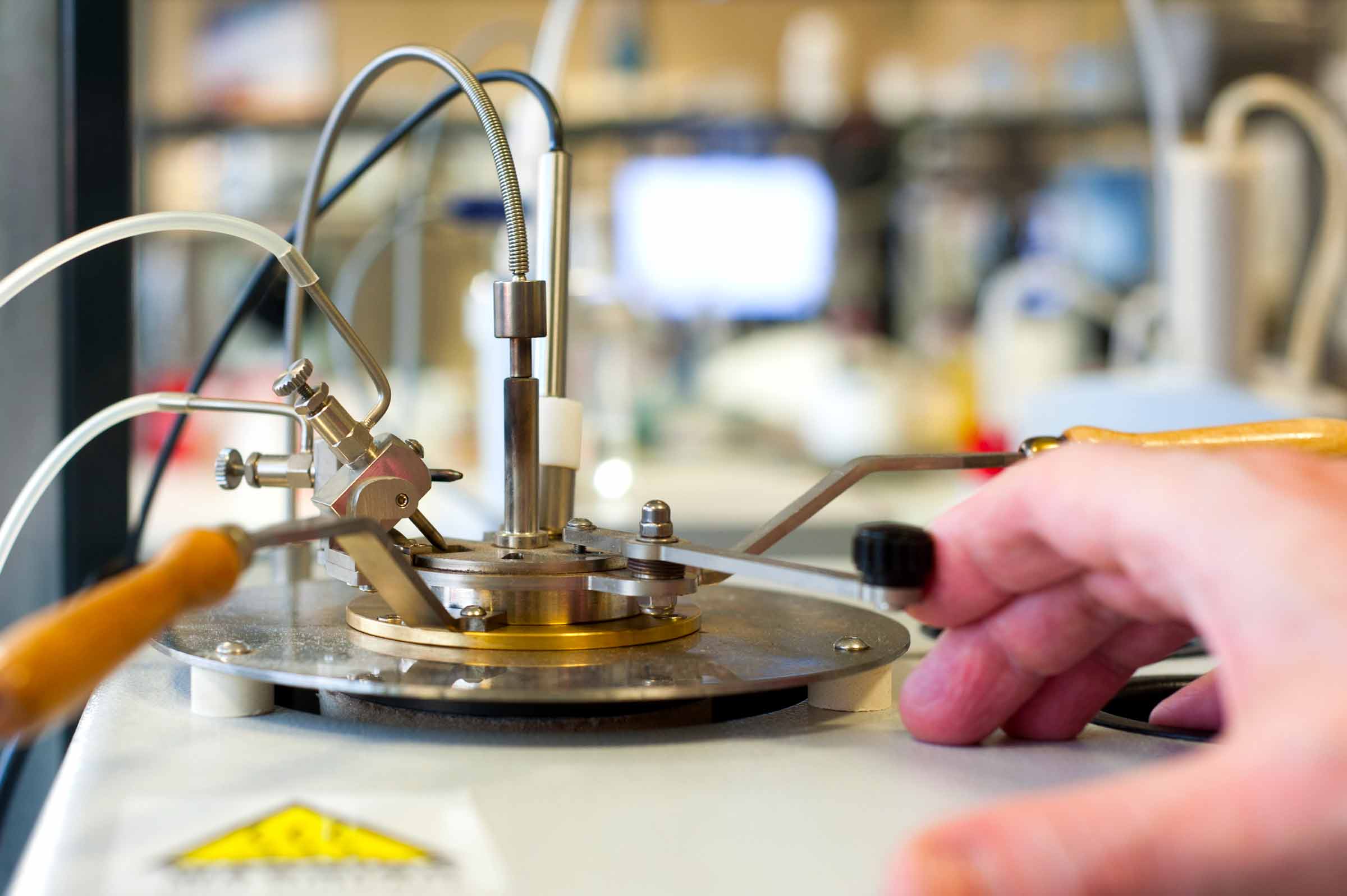
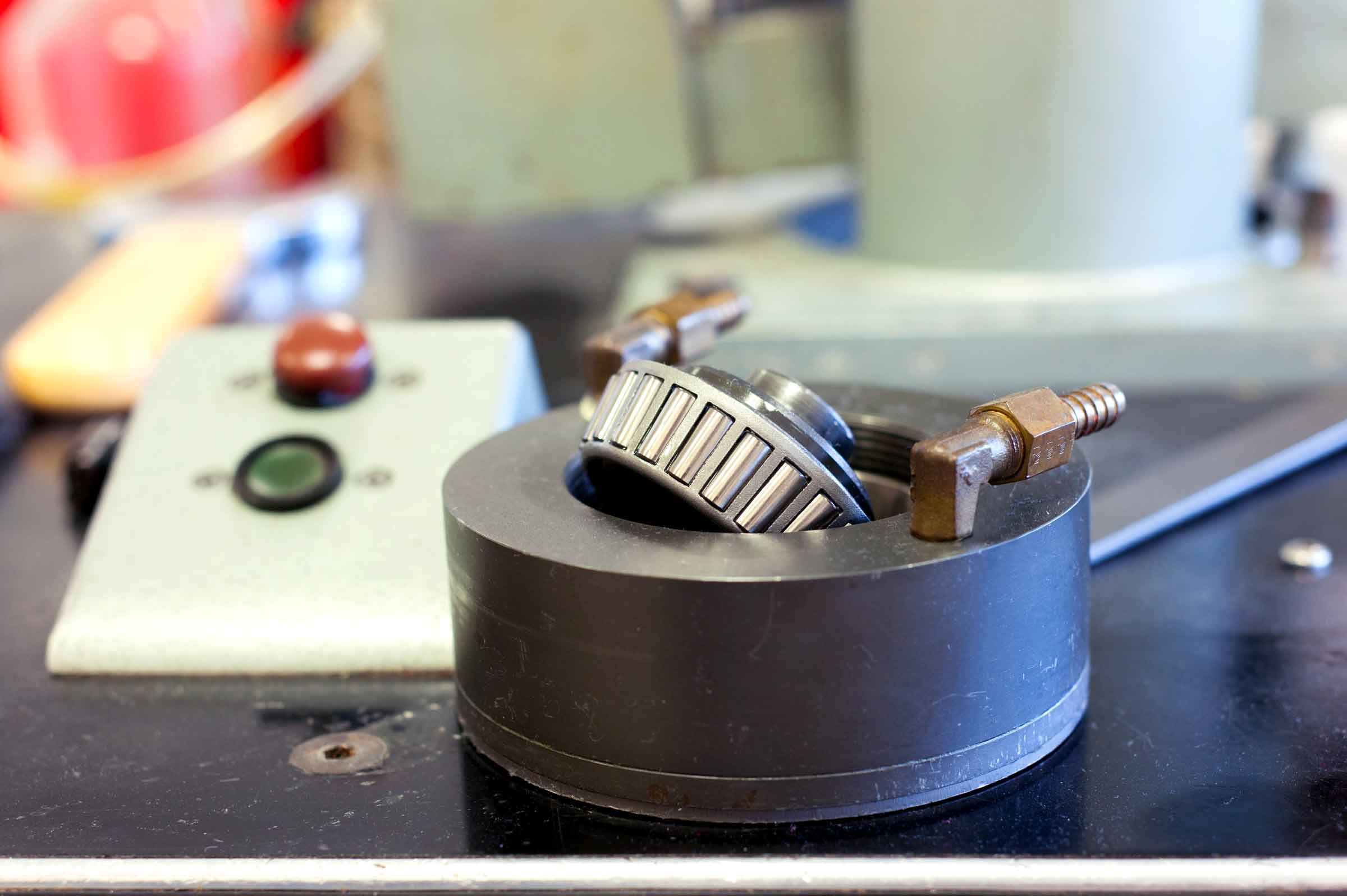
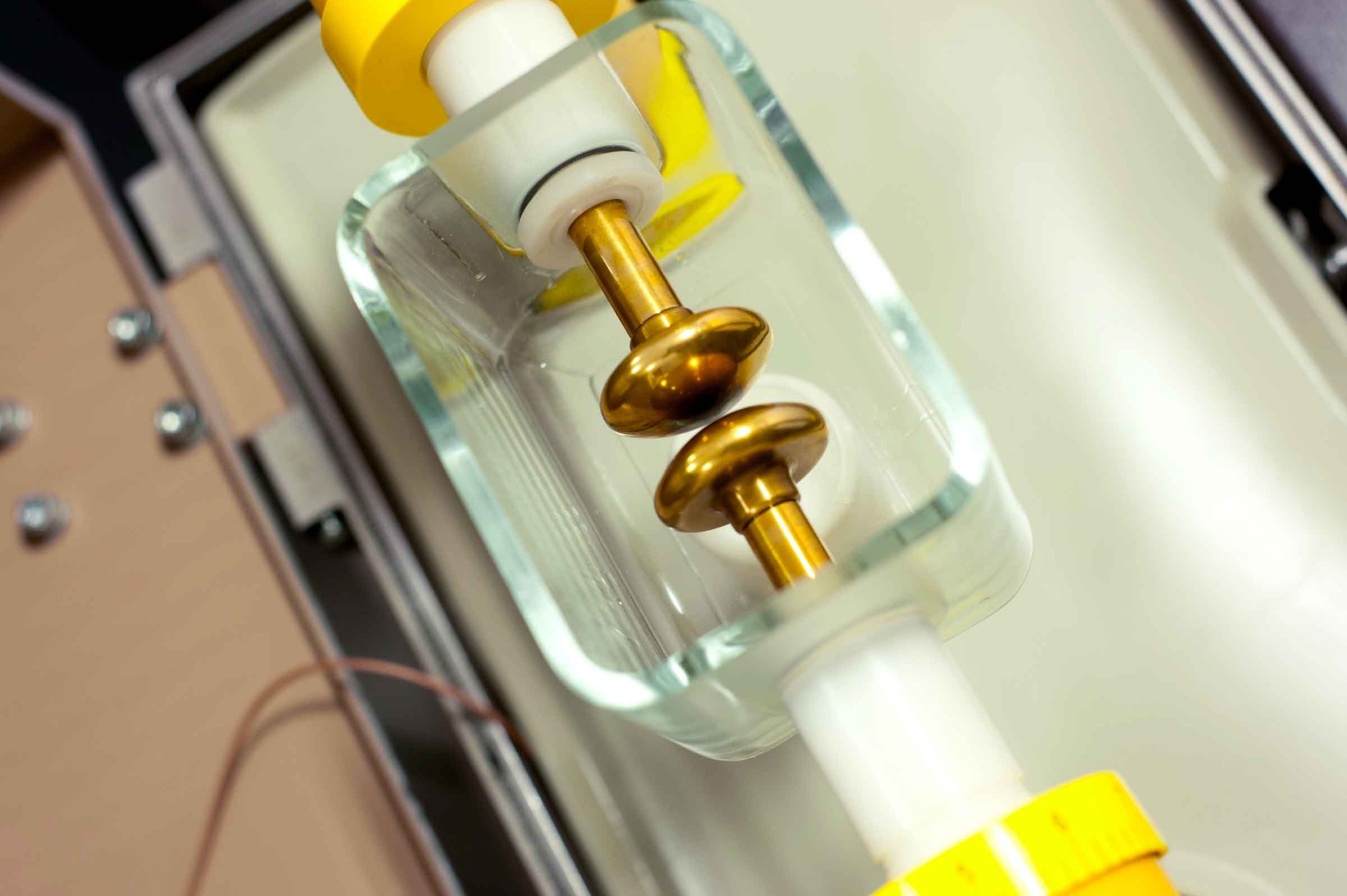
The S.R.V. (acronym of Schwingung, Reibung, Verschleiž namely Oscillating, Friction, Wear) measures the physical interactions between a lubricant and two specimens in a loaded contact in either rotational or linear oscillatory motion.
It determines the efficiency of lubricants and greases by measuring friction, anti-wear (AW) and extreme pressure (EP) properties simulating real metal to metal sliding contact.
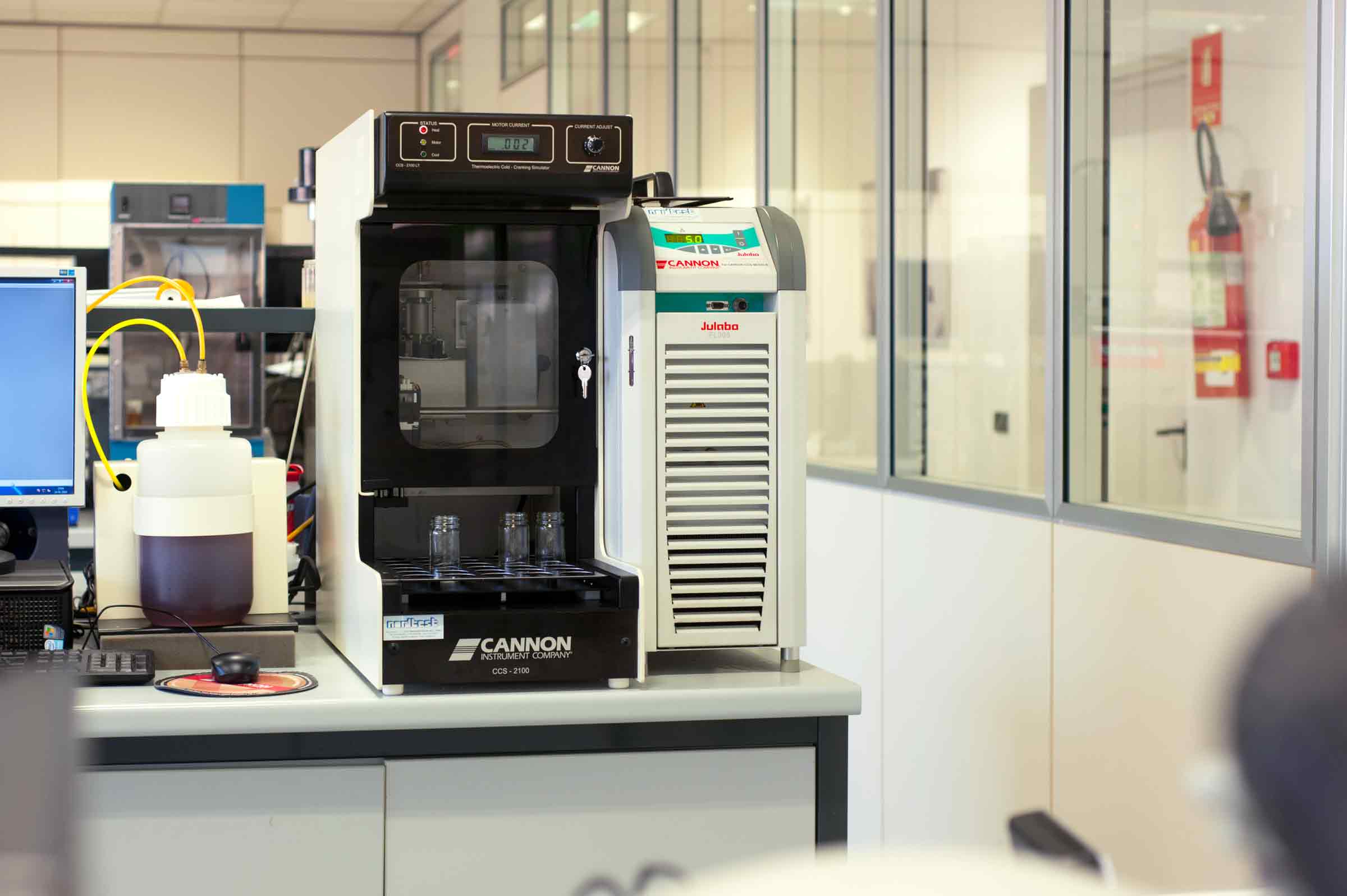
Cold Cranking Simulator (ASTM D5293) and Brookfield Viscometer (ASTM D2983) are used for the evaluation of apparent viscosity at low temperatures for engine lubricants (C.C.S.) according with SAE J300 or transmission lubricants (Brookfield) according with SAE J306. Lubricants pumpability at low temperatures is measured through the resistance generated by a pin dipped in the thermostat fluid at different temperatures.
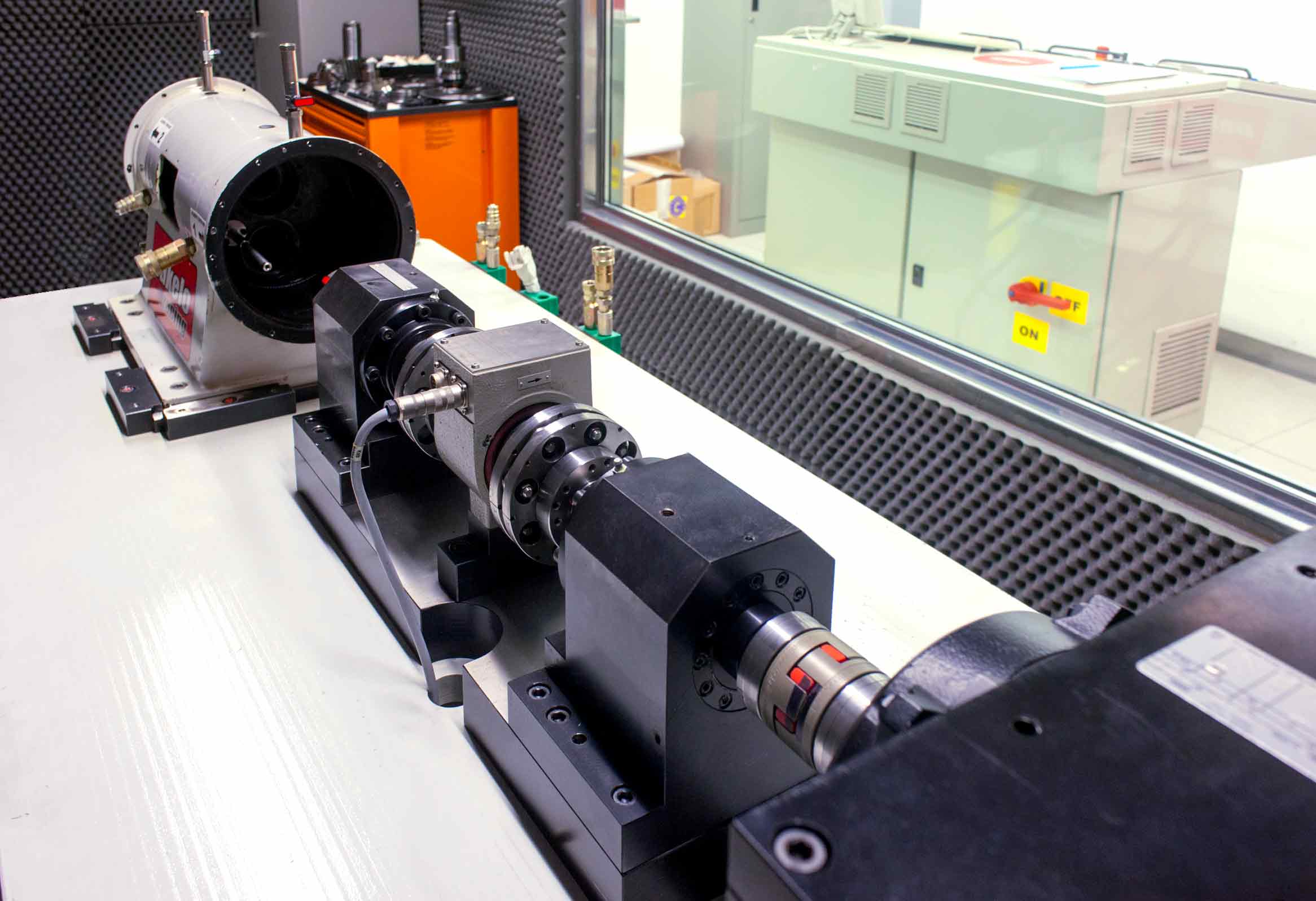
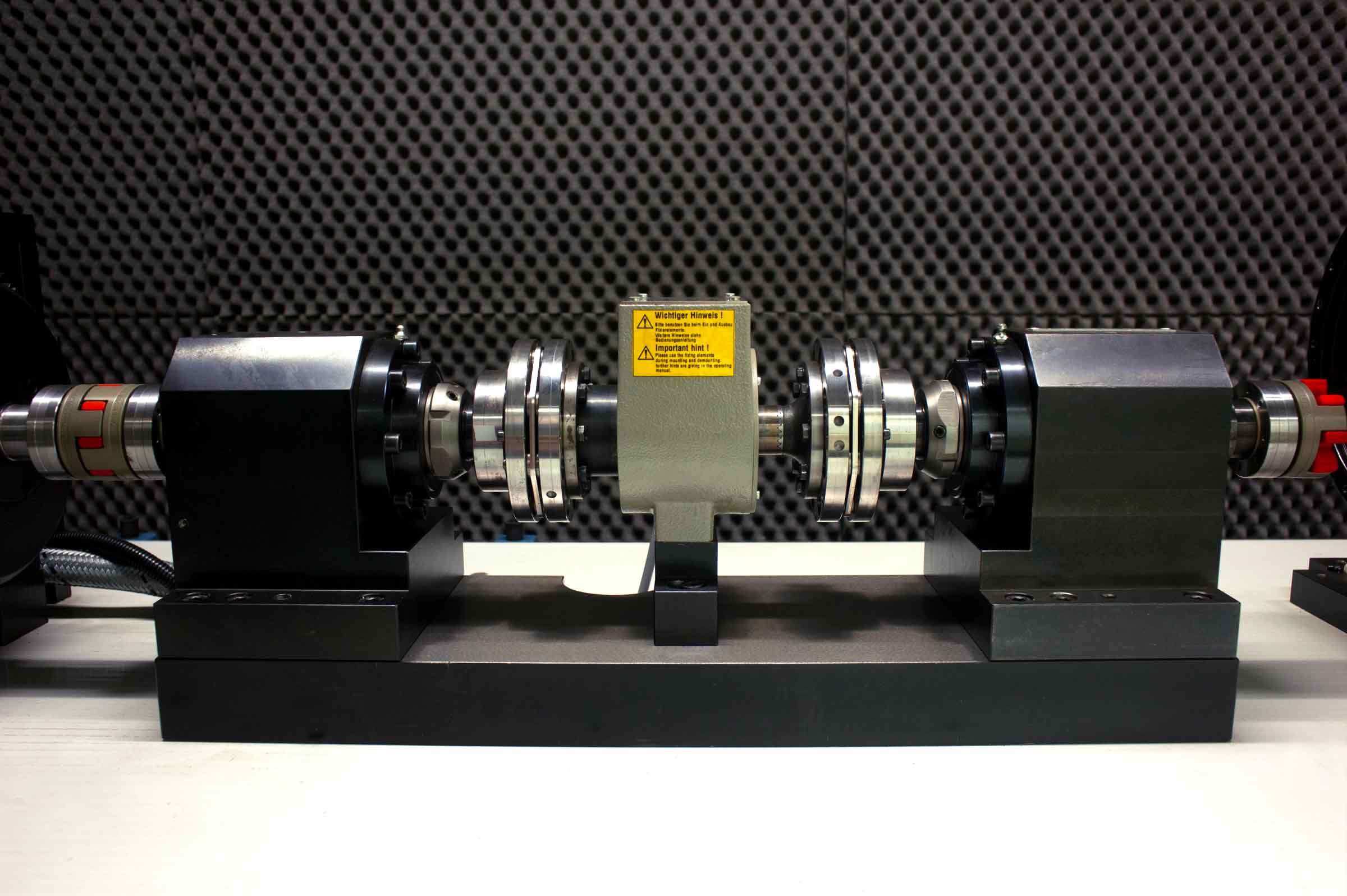
HT-HS measures dynamic viscosity in extreme shear rate conditions and high temperatures. The aim of the analysis is to measure the chemical/physical properties of different lubricant solutions under extreme shear rate conditions and at different temperatures.
The instrument has been designed to best simulate working conditions in all those parts exposed to high film fluid shear rate as it is common to rings/liners and connecting rod-crankshaft/bearings
Standard conditions (ASTM D 4683): T = 150°C / Shear Rate = 1.000.000s-1
Air Release time
Due to mechanic shaking all lubricants entrain air: this is bad for the lubrication and for the incompressibility of the fluid. In modern hydraulic systems the decantation period is reduced and it is important to guarantee air release rapidly. The test is based on the density change measured with an electronic balance.
The equipment and the connected test evaluate the foaming characteristics and collapse time in lubricating oils. An airflow is injected in the fluid. It is possible to evaluate the foaming tendency of engine lubricants up to 150°C and it is typically required for hydraulic fluids since this phenomenon affects the fluid compressibility.
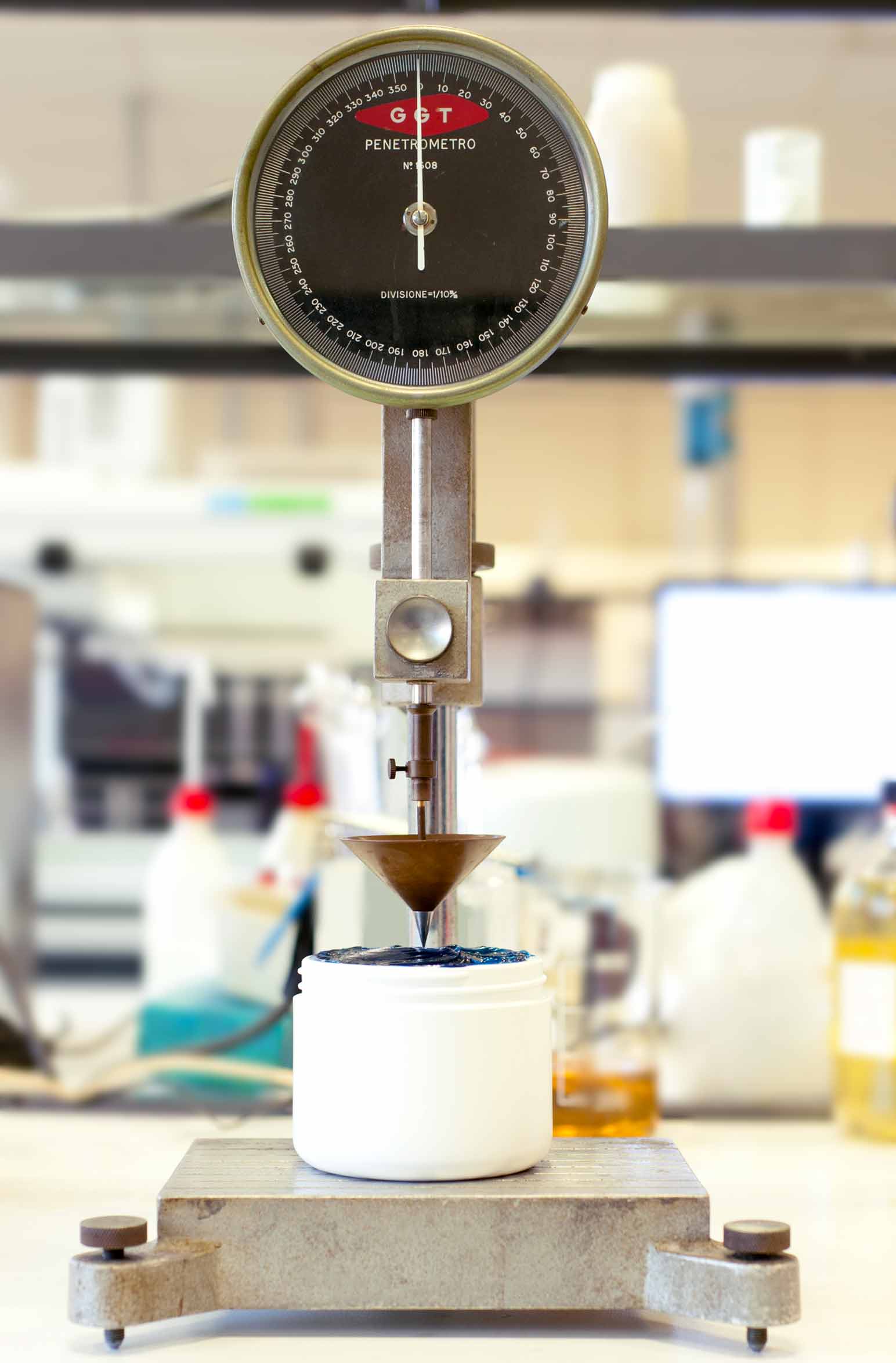
Extreme Pressure and Anti-Wear properties
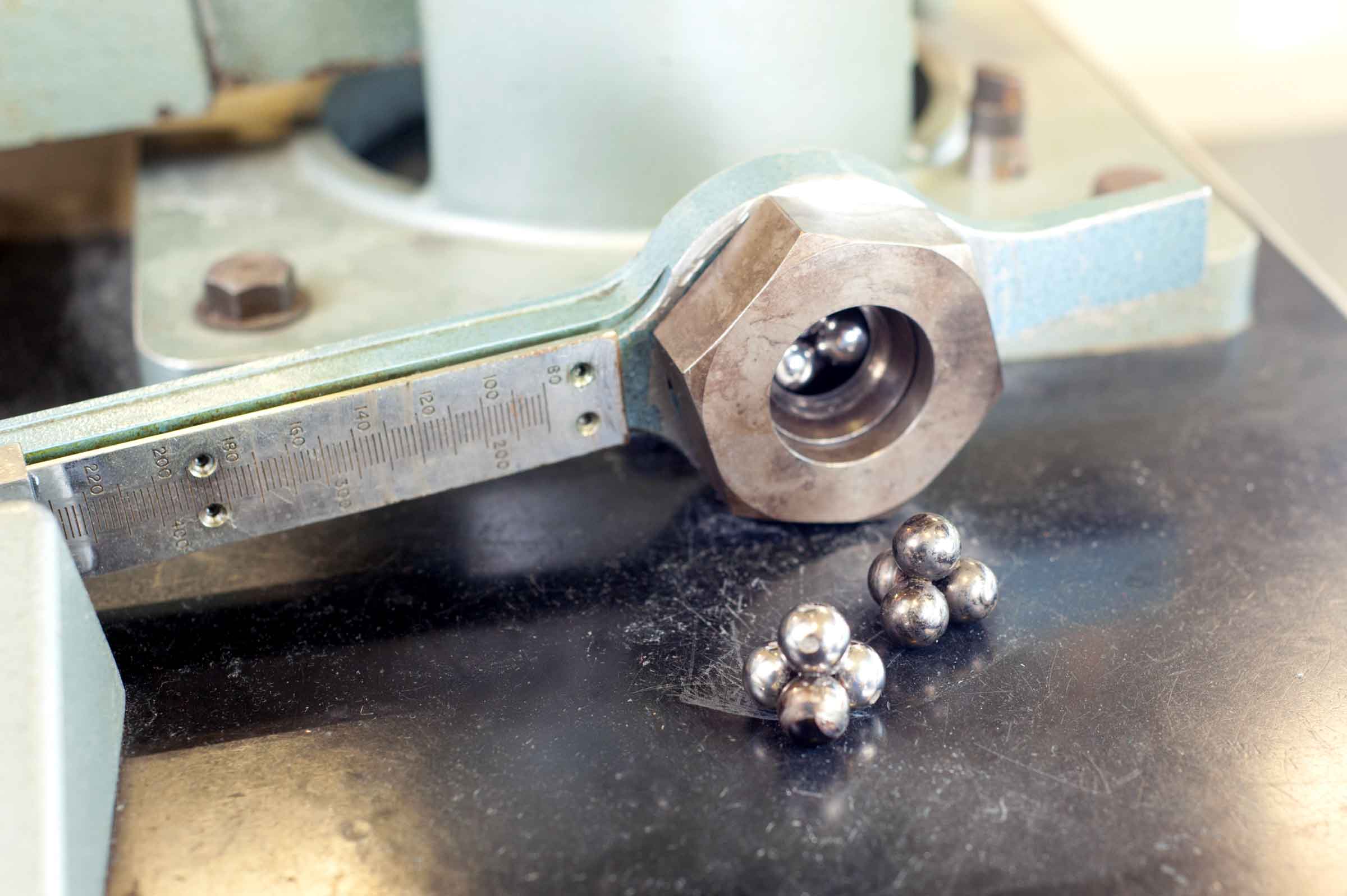
In this test one of the four balls brushes on the others creating extremely high superficial pressures. Enhancing the load, the lubricating conditions get more and more challenging till the final surface melts and welds. EP properties are identified analyzing the effect of heavy loads meanwhile lighter loads for longer periods of time allow to evaluate anti-wear properties.
The capacity to bear such specific loads and the anti-welding properties are essential characteristics in particular for transmissions and hydraulic lubricants.
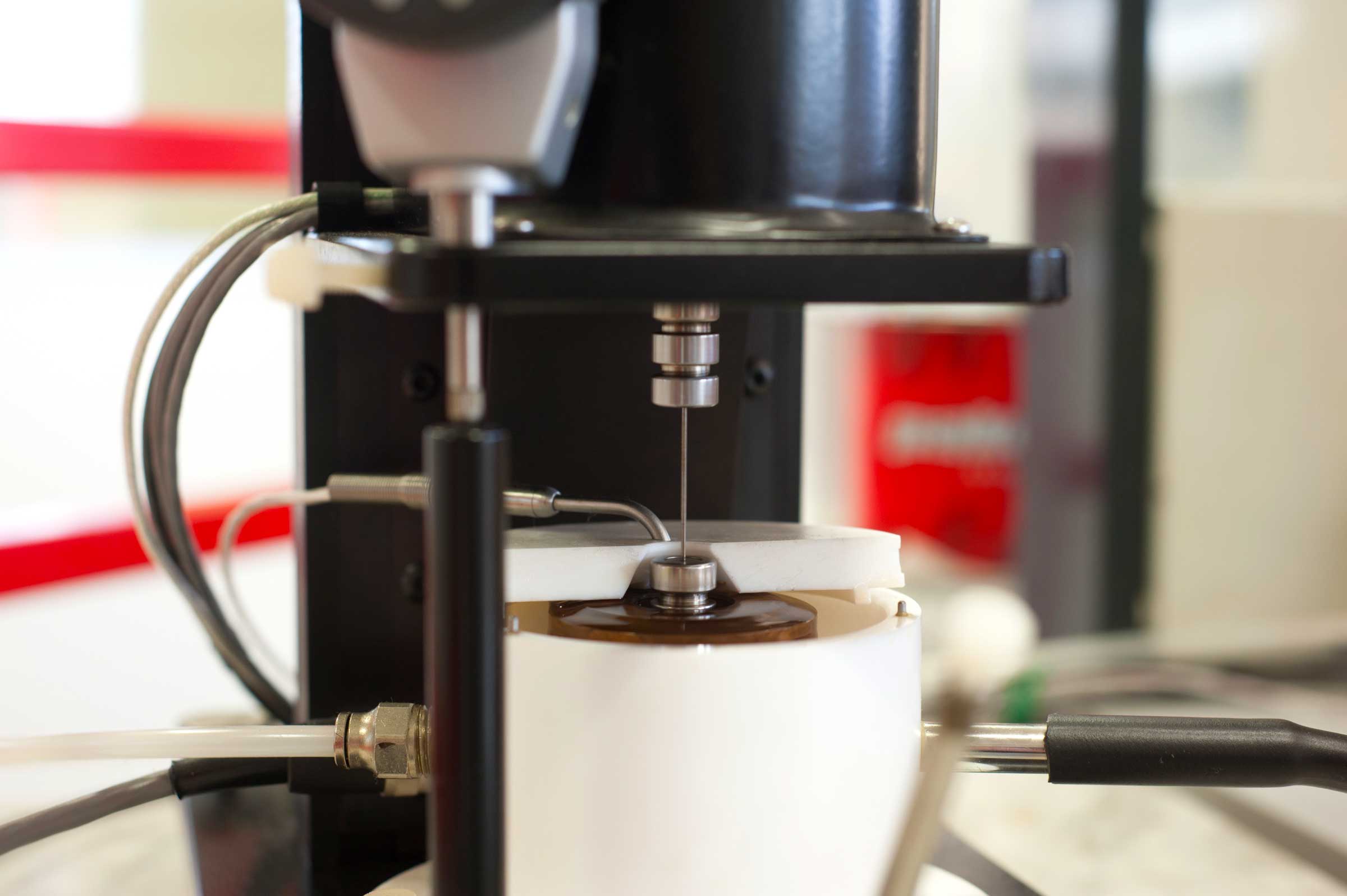
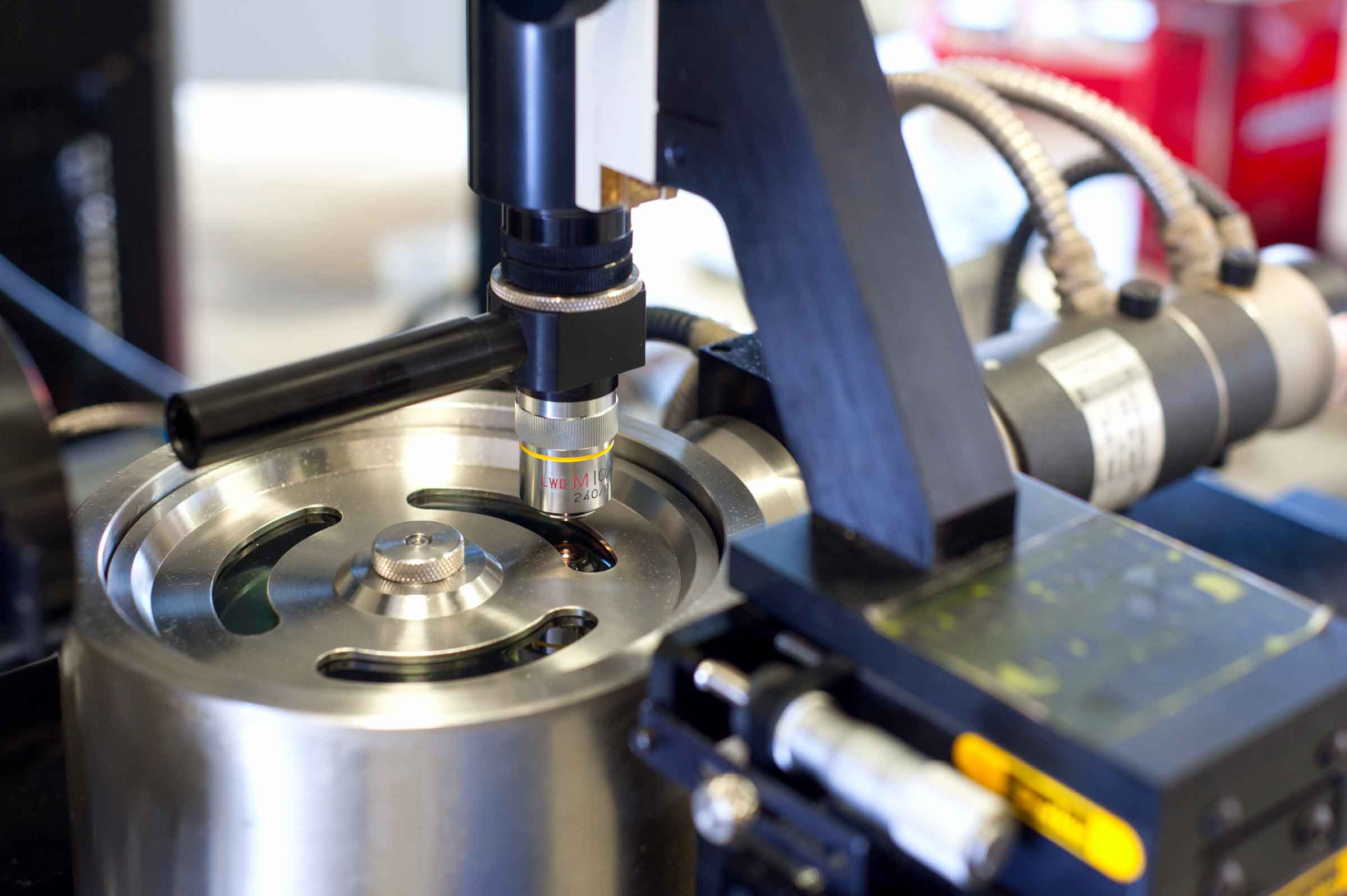
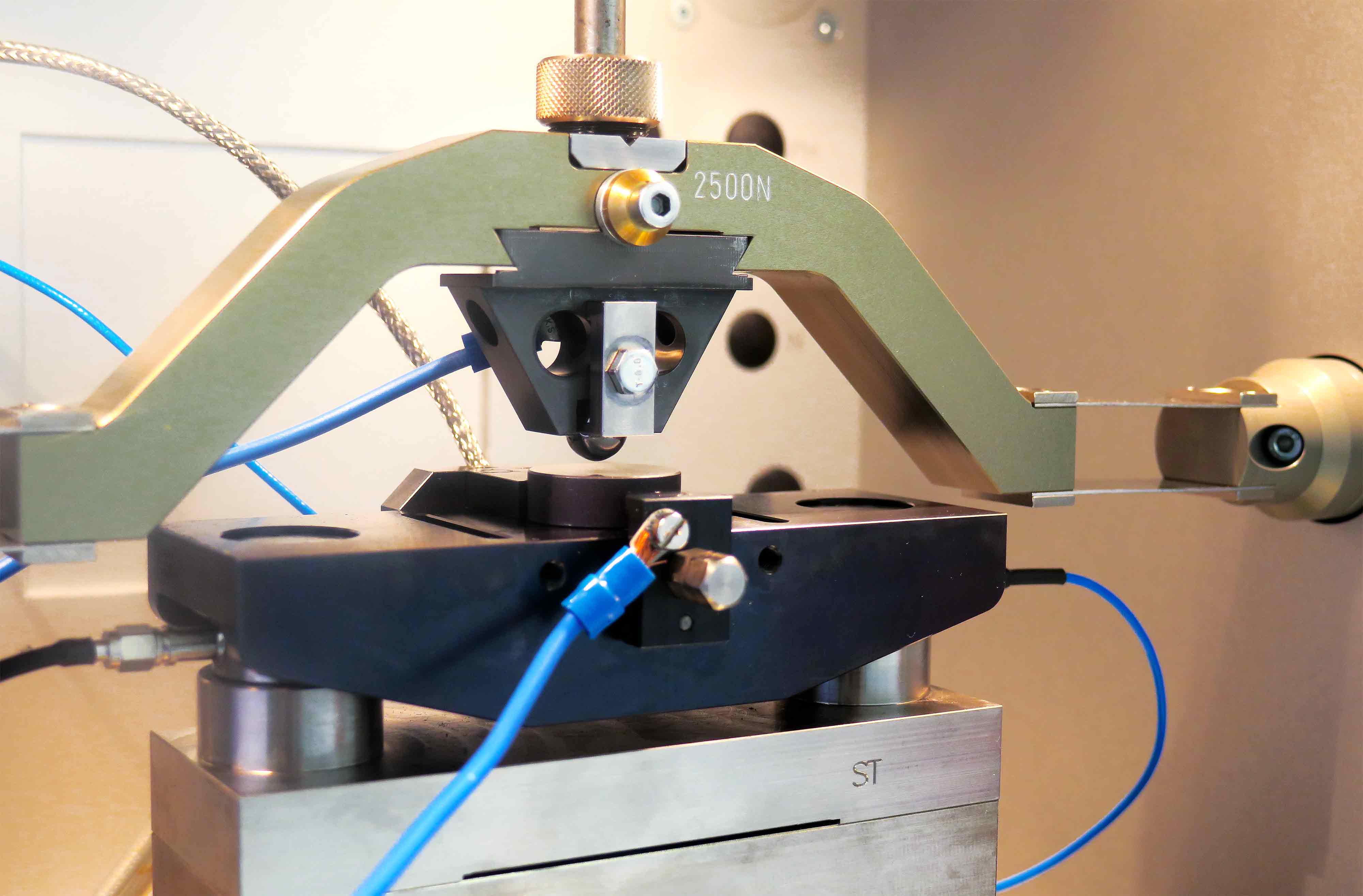
Analysis on Elastohydrodynamic Lubrication (Hertzian contact pressure)
E.H.L. instrument detects film thickness (in nanometers) and friction coefficients when there is deformation of surfaces on contact point. Measurement is made through an optical interferometric System. It is used in the analysis of friction modifiers’ properties, of fuel economy and for the initial formulation of high efficiency oils.
Sliding at low temperatures
The instrument measures the minimum temperature to have fluency in tilted tubes. This parameter helps in the identification of the service temperature threshold.
SECTORS
DEALERS
SECTORS
© Pakelo Motor Oil S.p.A. a s.u. 2025 - All rights reserved - P.Iva 01876150234 | Credits